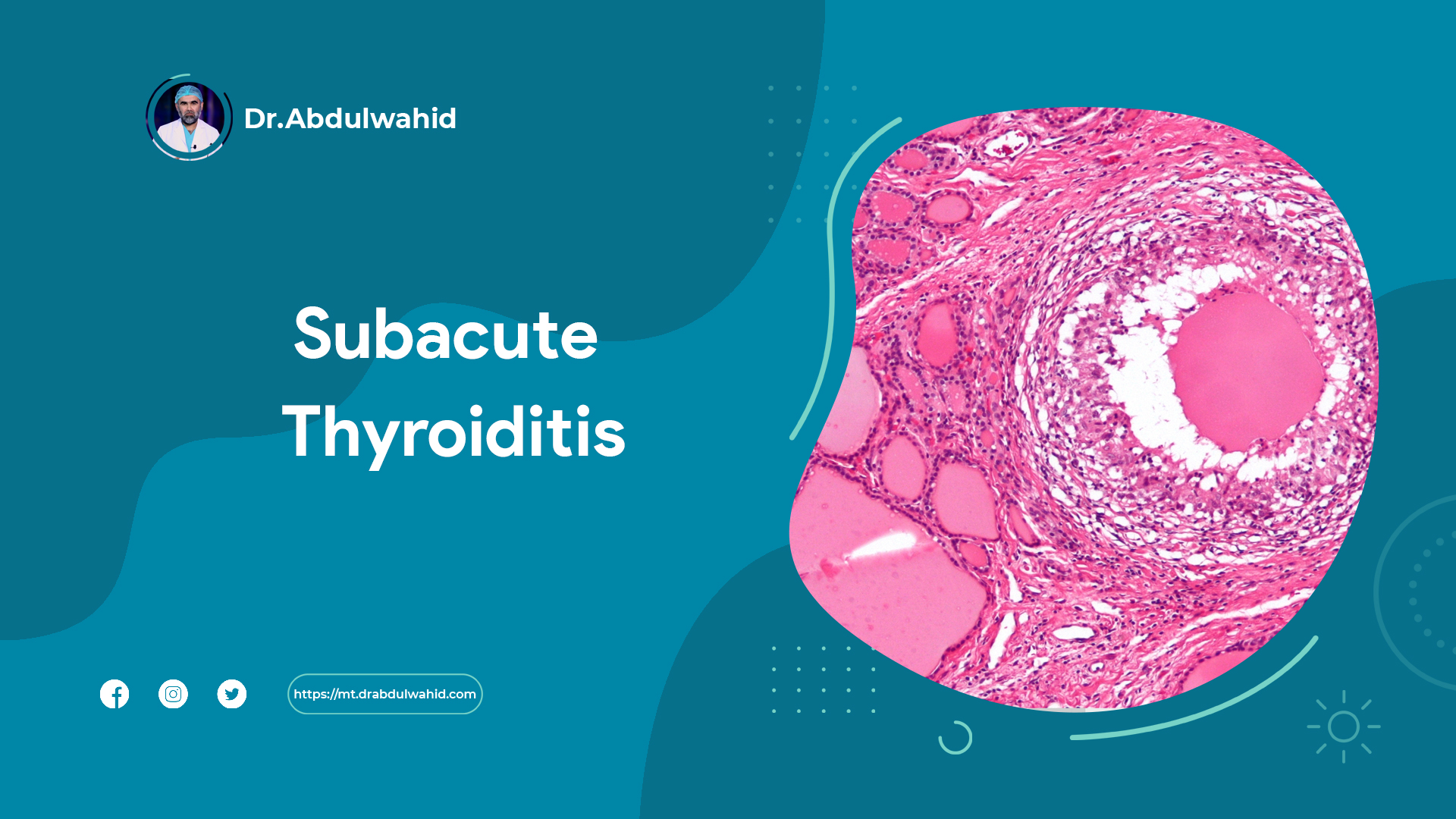
Definition
Subacute thyroiditis is an immune reaction of the thyroid gland that often follows an upper respiratory infection.
The thyroid gland is located in the neck, just above where your collarbones meet in the middle.
Alternative Names:
De Quervain's thyroiditis; Subacute nonsuppurative thyroiditis; Giant cell thyroiditis; Subacute granulomatous thyroiditis; Hyperthyroidism - subacute thyroiditis
Causes:
Subacute thyroiditis is an uncommon condition. It is thought to be the result of a viral infection. The condition often occurs a few weeks after a viral infection of the ear, sinus, or throat, such as mumps, the flu, or a common cold.
Subacute thyroiditis occurs most often in middle-aged women with symptoms of a viral upper respiratory tract infection in the past month.
Symptoms:
The most obvious symptom of subacute thyroiditis is pain in the neck caused by a swollen and inflamed thyroid gland. Sometimes, the pain can spread (radiate) to the jaw or ears. The thyroid gland may be painful and swollen for weeks or, in rare cases, months.
Other symptoms include:
• Tenderness when gentle pressure is applied to the thyroid gland
• Difficulty or painful swallowing, hoarseness
• Fatigue, feeling weak
• Fever
The inflamed thyroid gland may release too much thyroid hormone, causing symptoms of hyperthyroidism, including:
• More frequent bowel movements
• Hair loss
• Heat intolerance
• Irregular (or very light) menstrual periods in women
• Mood changes
• Nervousness, tremor (shakiness of the hands)
• Palpitations
• Sweating
• Weight loss, but with increased appetite
As the thyroid gland heals, it may release too little hormone, causing symptoms of hypothyroidism, including:
• Cold intolerance
• Constipation
• Fatigue
• Irregular (or heavy) menstrual periods in women
• Weight gain
• Dry skin
• Mood changes
Thyroid gland function often returns to normal over a few months. During this time you may need treatment for your underactive thyroid. In rare cases, hypothyroidism may be permanent.
Investigations:
Laboratory tests that may be done include:
• Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) level
• T4 (thyroid hormone, thyroxine) and T3 level
• Radioactive iodine uptake
• Thyroglobulin level
• Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)
• C reactive protein (CRP)
• Thyroid ultrasound
In some cases, a thyroid biopsy may be done.
Treatment:
The goal of treatment is to reduce pain and treat hyperthyroidism, if it occurs. Drugs such as aspirin or ibuprofen are used to control pain in mild cases.
More serious cases may need short-term treatment with drugs that reduce swelling and inflammation, such as prednisone. Symptoms of an overactive thyroid are treated with a class of drugs called beta-blockers.
If the thyroid becomes underactive during the recovery phase, thyroid hormone replacement may be needed.
Outlook (Prognosis):
The condition should improve on its own. But the illness may last for months. Long-term or severe complications do not often occur.
The condition is not infectious. People cannot catch it from you. It is not inherited within families like some thyroid conditions.
When to Contact a Medical Professional?
Call your health care provider if:
• You have symptoms of this disorder.
• You have thyroiditis and symptoms do not improve with treatment.
Prevention:
Vaccines that prevent viral infections such as the flu may help prevent subacute thyroiditis. Other causes may not be preventable.
Resource : PennMedicine.org